The energy loss due to a sudden contraction, such as that sketched in the figure, is calculated from $$h_L = k \frac{v_2^2}{2g}$$ where $v_2$ is the velocity in the small pipe downstream from the contraction.
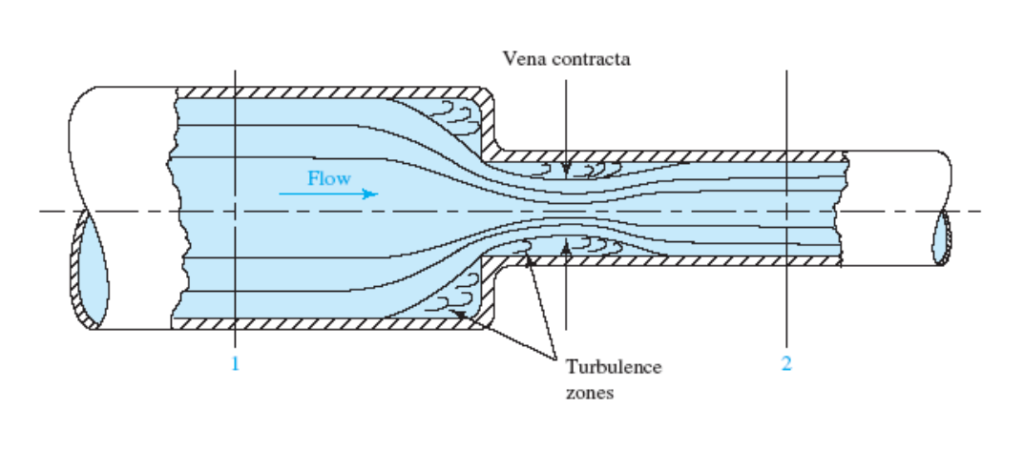
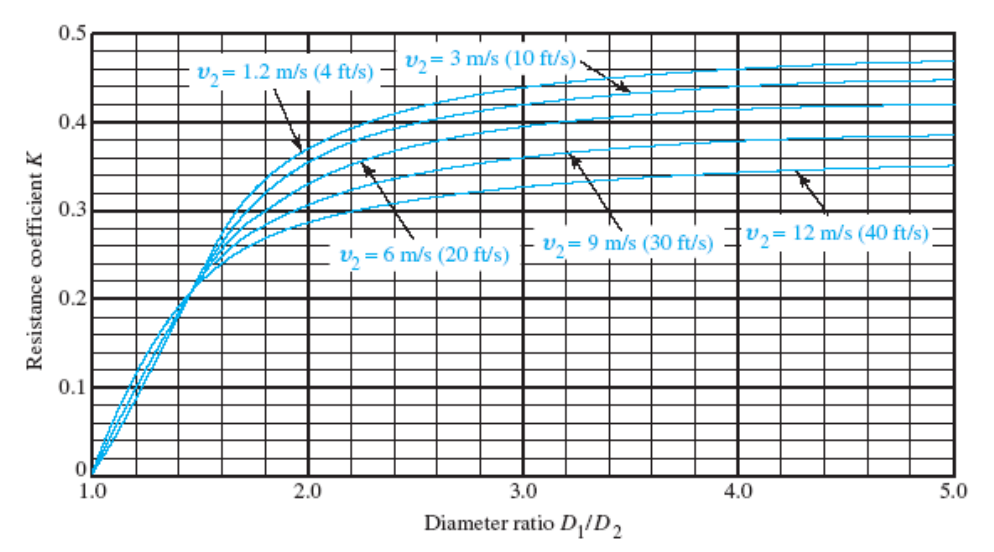
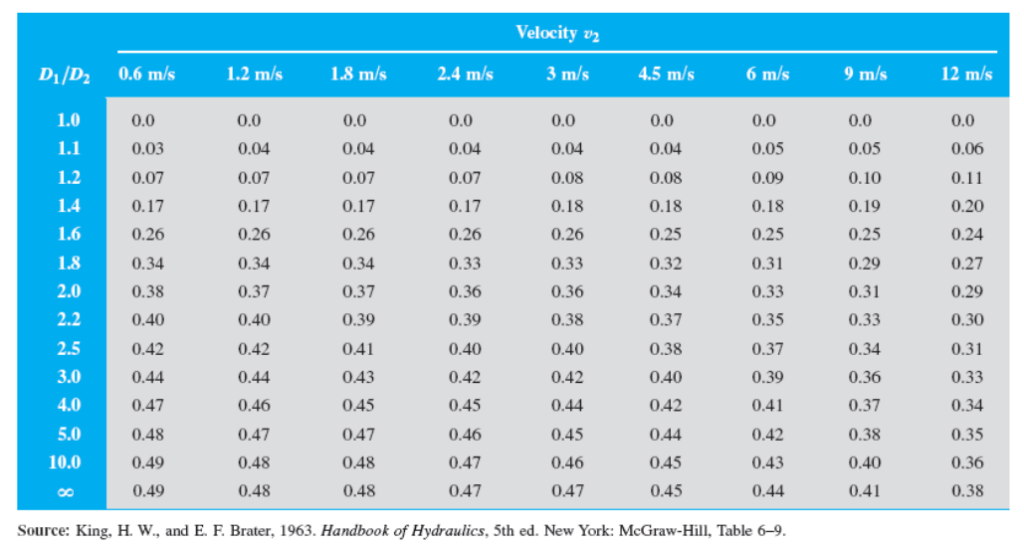
The energy loss due to a sudden contraction, such as that sketched in the figure, is calculated from $$h_L = k \frac{v_2^2}{2g}$$ where $v_2$ is the velocity in the small pipe downstream from the contraction.


